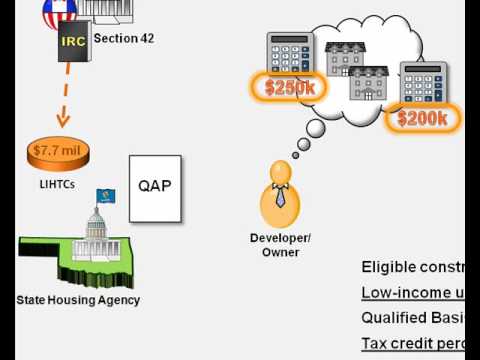
So you have a company that's been successful and has generated a lot of revenue over the years. - When you generate lots of revenue, that means you owe the IRS a lot of taxes. - As part of the 1986 Tax Reform Act, Congress created section 42 of the Internal Revenue Code, otherwise known as the low income housing tax credit. - Under this low income housing tax credit program, this company can contribute capital to or invest in affordable housing projects that will enable low income families to live in quality housing while paying less than the fair market rent. - In return for contributing this capital, the company is able to claim tax credits that will reduce its federal income tax liability. - Now obviously, the present value of the reduction in tax liability needs to be greater than the capital contributed for the program to be worthwhile to the investor company. - So how exactly though does the program work? What are the mechanics? Let's talk about those. - First of all, even though the tax credits offset federal tax liability, the responsibility for administering the program is actually delegated to state housing agencies. - We use Oklahoma for our example. - As defined in the code, each state receives a pool of tax credits based on the population of the state. - So in 2010, the population of Oklahoma is approximately three point six seven million people. - There is a factor by which the states multiply their population to identify their tax credit pool for the year. - In 2010, that factor is two dollars and ten cents. - Three point six seven million times two dollars and ten cents equals approximately seven point seven million dollars in low-income housing tax credits to be...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing When 8850 Form Taxpayer