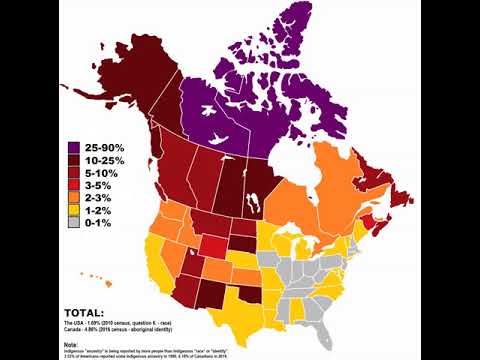
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the indigenous peoples of the United States, except Hawaii. There are over 500 federally recognized tribes within the U.S., about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. The term "American Indian" excludes Native Hawaiians and some Alaskan Natives, while Native Americans, as defined by the US census, are American Indians plus Alaska Natives of all ethnicities. Native Hawaiians are not counted as Native Americans by the US census, instead being included in the census grouping of Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander. The ancestors of modern Native Americans arrived in what is now the United States at least 15,000 years ago, possibly much earlier, from Asia via Beringia. A vast variety of peoples, societies, and cultures subsequently developed. Native Americans were greatly affected by the European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, and their population declined precipitously due to introduced diseases, warfare, and slavery. After the founding of the United States, many Native American peoples were subjected to warfare, removals, and one-sided treaties, and they continued to suffer from discriminatory government policies into the 21st century. Since the 1960s, Native American self-determination movements have resulted in changes to the lives of Native Americans, though there are still many contemporary issues faced by Native Americans today. There are over five million Native Americans in the United States, 78% of whom live outside reservations. When the United States was created, established Native American tribes were generally considered semi-independent nations, as they generally lived in communities separate from British settlers. The federal government signed treaties at a government-to-government level until the Indian Appropriations Act of 1871 ended recognition of independent Native Nations and started treating them as domestic dependent nations subject to federal law. This law did preserve the rights...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Where 8850 Form Applicant