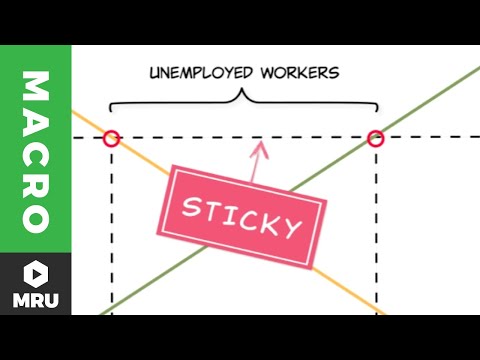
Today we're going to look at cyclical unemployment, unemployment correlated with the ups and downs of the business cycle. Using our friend, the Fred database, it's easy to see that unemployment increases during a recession when the economy is shrinking or growing only very slowly. Indeed, low growth and high unemployment are part of what define a recession. Lower growth is usually accompanied by high unemployment for two reasons. First, when GDP is falling or growing more slowly than expected, firms often lay off workers, which generates unemployment. The second reason is slightly more subtle. Higher unemployment means that fewer workers are producing goods and services, and when workers are sitting idle, it's likely that capital is also sitting idle. In an economy with idle labor and capital, well, it can't be maximizing growth. Although unemployment is clearly correlated with the business cycle, the exact reasons why are debated by economists. To see some of the issues, notice, for example, that unemployment typically spikes quickly when growth declines, but then it returns to more normal levels only slowly. The unemployment rate spiked in 2008, for example, as the economy declined. By 2010, the economy was actually growing at a slow but steady rate of around 2% per year, but unemployment didn't return to pre-recession levels for another five years. Why did it take so long for the unemployment rate to return to more normal levels? Think about a typical market, say the market for apples. Unemployed apples, in this case, would be apples that aren't being bought. Now, in a situation with high apple unemployment, you'd have a higher quantity supplied than the quantity demanded at the current price. So what would you expect to happen in this situation? Well, ordinarily, the price of apples would drop until the quantity...
Award-winning PDF software





Video instructions and help with filling out and completing Who 8850 Form Unemployment